The SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) methodology promises to transform the way an organisation develops its products, from the development teams right through to top management. The method knows how to adapt to needs and offers different deployment configurations. It remains highly structured, right down to its implementation schedule, which we recommend you follow to ensure the success of the transformation (but that’s a subject for a further article!). The SAFe method is full of concepts, roles and processes, and the sheer number of them doesn’t make it easy to understand a method that isn’t all that complex in the way it works. Let’s take a look at the key elements of the method, namely its different organisational layers, which enable all the layers of the company to be aligned.
Agile Release Train
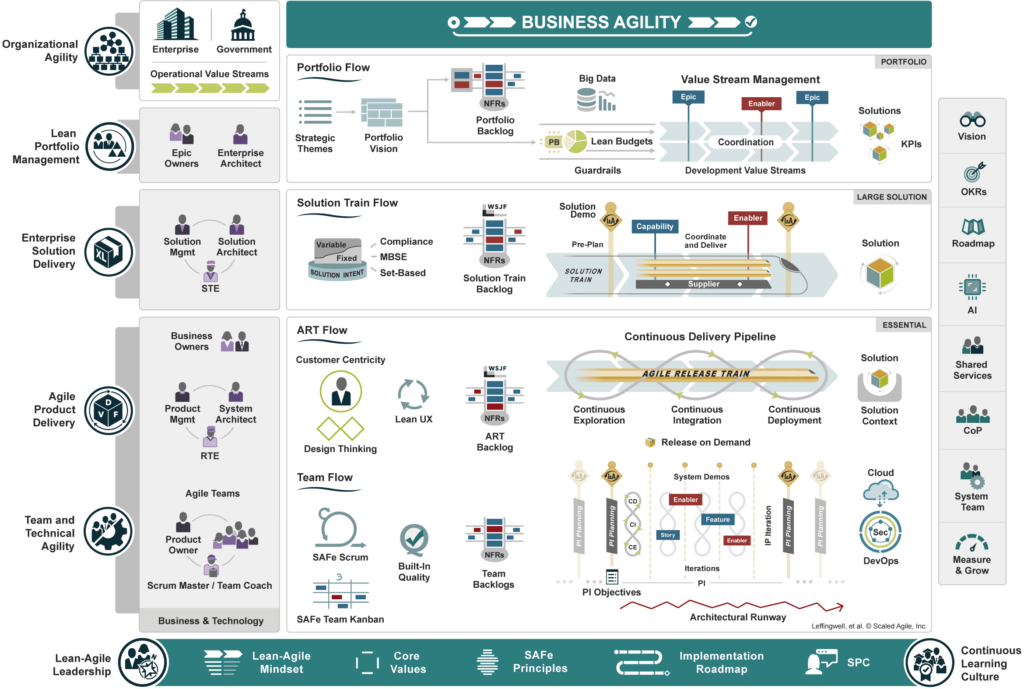
The Agile Release Train (ART) is the heart of SAFe. Quite simply, it enables several teams to move forward together, synchronised with sprints of the same duration, whether they are working with Scrum or Kanban. ART enables teams representing the different business areas required to advance a large-scale project to move forward together.
To align the teams, it’s not enough to give them a starting signal. This takes the form of a ceremony specific to SAFe: the Program Increment Planning (PI Planning). All the teams get together to launch the work of the next Sprints: ideally 4, for a PI Planning that recurs every 8 weeks.
The PI Planning is the key ceremony in the SAFe method, and an important moment in the success of the process. It can take place over several days, face-to-face. So it’s a major constraint for the teams, and a key part of this methodology.
What’s more, at the end of each sprint, the System Demo ceremony provides an opportunity to review the sprint together and make any necessary adjustments. The System Demo does not exempt each team from holding its own Demo or Sprint Review ceremony, as well as its own retrospectives (see Scrum).
Solution Train
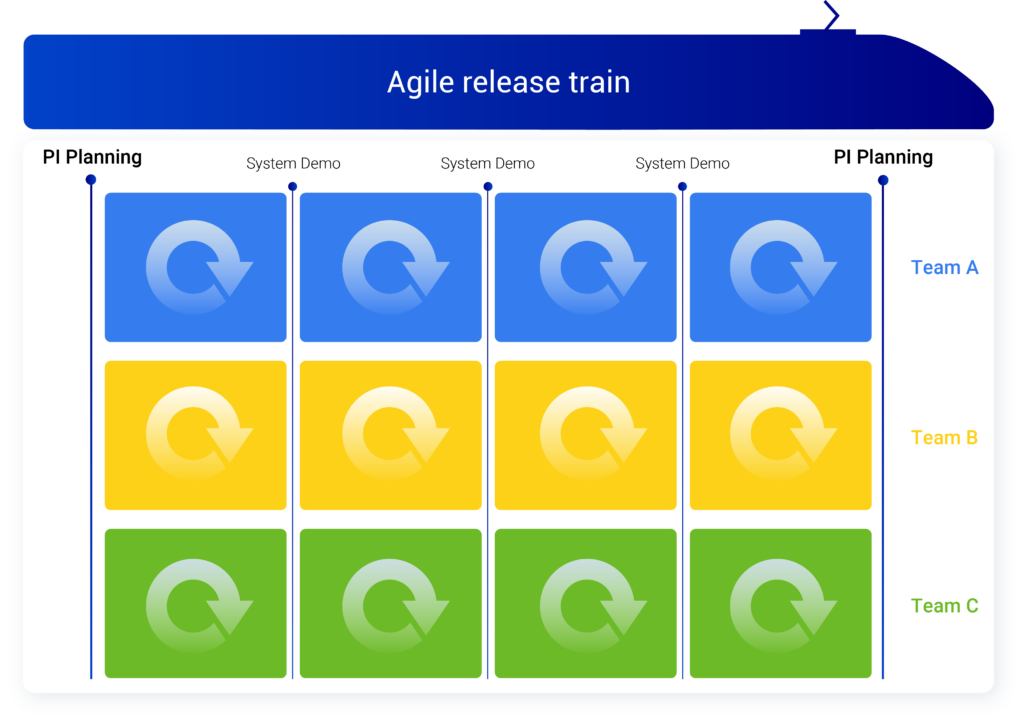
For some large projects, ART is not enough to synchronise all the teams, because there are too many of them. PI Planning would be too complex to implement. SAFe therefore proposes to add an organisational level through the Solution Train, which will simply be made up of several ARTs:
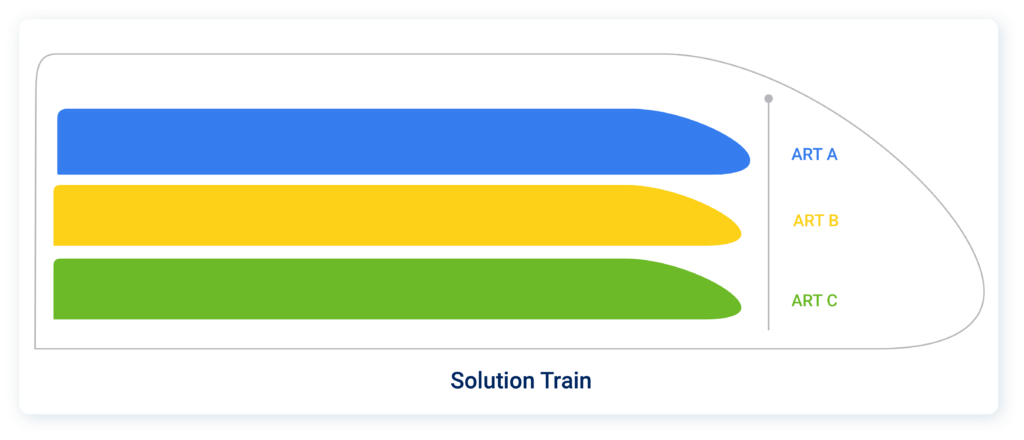
Le Solution Train permet de faire avancer ensemble plusieurs Agile Release Trains. Il se base sur les mêmes concepts que l’ART pour la synchronisation. PI Planning, System Demo.
Ainsi, afin de comprendre la terminologie de SAFe, chaque équipe travaille sur un produit avec une méthode agile simple (Scrum, Kanban). Ensuite, un Programme et son Agile Release Train contient plusieurs produits et les équipes associées. Au niveau du dessus, la Solution (ou Large Solution) permet de synchroniser plusieurs programmes et leurs ART.
Portfolio
Left to the discretion of each company by the other @scale agile methods, the Portfolio level is a specific feature of SAFe which enables strategic, business and budgetary aspects to be aligned with development trains.
In simple terms, SAFe’s Portfolio layer provides governance to ensure that development trains are always aligned with budgets and strategy. In concrete terms, the players at this level have a sort of Backlog of strategic initiatives which will influence the development trains at a lower level. Budgetary constraints will also have an influence on the construction of these trains.
Of course, here, decisions are fuelled by multiple data sources, the company’s big data, with the right tools to clearly visualise the important consolidated data.
Everything you need to know about SAFe and the market
To find out more about SAFe and its associated software market, Spectrum Groupe is preparing an update of its study on agility and the project management market through to agility at scale for September. Stay tuned to discover de 2024 edition!