There’s no doubt that the Cloud is still booming, and it’s a trend that will last. It is revolutionizing the way organizations used to work. However, there are still fears, reticence and even preconceived ideas about hosting data in the Cloud. Yet today, this type of hosting offers a wide range of possibilities to meet everyone’s needs. The term Cloud is no longer sufficient to define what it stands for. Let’s take a look at what the “Cloud” has to offer.
The Cloud offers significant advantages to organizations, such as reduced costs for IT infrastructure and systems maintenance, as well as transparent application updates and systematic access to the latest technologies. These advantages enable companies to gain in agility and flexibility, rationalize costs and reinforce the security of information systems, optimize resources, innovate… (See our article about the benefits of moving to the Cloud).

The Cloud service models
Cloud computing offers a number of different service models. The most popular models on the market are SaaS, IaaS and PaaS, depending on the desired service layer.
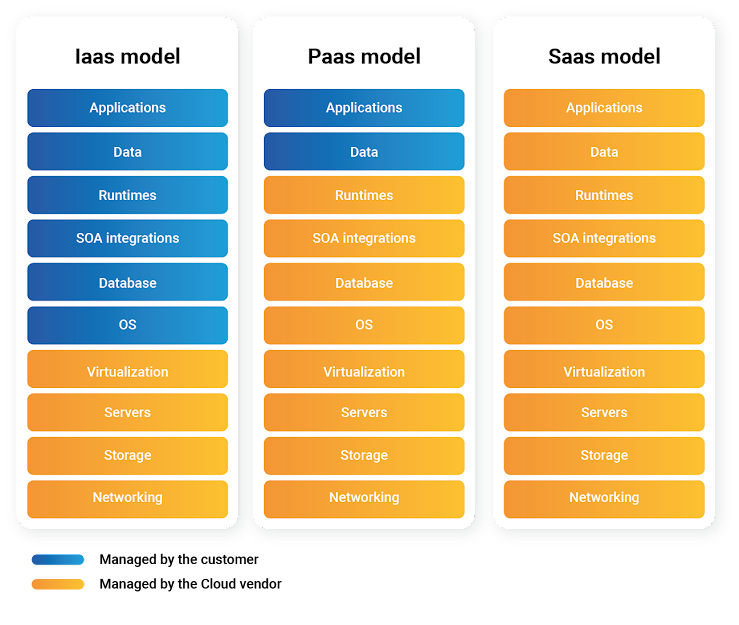
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): this is the basic layer of the Cloud service model. It involves renting virtual machines located in data centers owned by the IaaS provider. In effect, the supplier provides the basic infrastructure, i.e. machines, servers, network, and users can install and manage their own operating systems… This requires greater responsibility on the part of users to manage and maintain resources.
PaaS (Platform as a Service): PaaS provides users with a complete development platform. This means they can manage their data and applications. Runtime, integrations, databases, networking, storage… are all managed by the provider.
SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS is the most familiar model for end users. Here, the supplier manages the entire infrastructure, right down to the application and its data. SaaS allows companies to concentrate entirely on the application itself, with the software publisher taking care of hosting the product with its supplier.
The different type of data hosting
Cloud computing covers different types of hosting, such as private Cloud, public Cloud, multicloud and many more. Each has its own specific features.
Public Cloud
In the public cloud, data is not hosted by the company itself, but instead by a third-party Cloud service provider. This is the Cloud we’re all familiar with, the most widespread, and the least expensive. Data remains secure, and can (should!) be duplicated/backed up by the provider to ensure that customer data is never lost, even in the event of an accident in the physical infrastructure.
The private Cloud
The Cloud is first and foremost a way of developing applications. The concept can also be used internally. With a private Cloud, data is hosted on servers reserved for the client company. They may even belong to the company and be located on its premises. Private Clouds come in several forms:
Managed private Cloud: data is hosted by the company, but the IT infrastructure is managed by a partner.
Hosted private Cloud: data is hosted and managed by a Cloud service provider. This is the most widely used type.
Community private Cloud: This is a shared private Cloud. It generally concerns companies belonging to the same group.
Hybrid Cloud:
The hybrid Cloud is the simultaneous use of two types of Cloud. The most common combination is a public Cloud combined with a private Cloud. In this case, the company can host sensitive data in the private Cloud and the rest in the public Cloud. The hybrid Cloud enables the organization to benefit from the advantages of both types of Cloud.
Multicloud:
Multicloud refers to the use of private or public Clouds from different suppliers. Multicloud optimizes performance and reliability by distributing work across different Cloud providers.
The Atlassian Cloud
Atlassian uses the public Cloud to host its products under “Cloud”-stamped licenses. Data is hosted on Amazon Web Services (AWS), a major market player.

Atlassian offers 3 Cloud subscriptions:
The Cloud Standard subscription, is designed for all teams and offers advanced features compared to the Free subscription. The Cloud Standard subscription offers a storage level of 250GB, and also features “data residency” functionality which allows companies to specify where they want their data to be hosted in the Atlassian Cloud. This can help meet corporate policies and compliance requirements.
The Cloud Premium subscription, offers advanced features and additional capabilities compared to the Cloud Standard subscription. Companies benefit from 24/7 Premium support and unlimited storage. The Cloud Premium subscription is designed for businesses that need advanced features and require a high level of performance and support.
The Cloud Enterprise subscription is designed to meet the needs of large enterprises with complex governance, security and scalability requirements. It offers high-end features and extensive customization options. This subscription meets the specific requirements of large enterprises. For the Enterprise subscription, data is hosted in the European Union and the United States.
Atlassian’s service level remains on the AWS public Cloud, which can provide all the reliability and security required. Atlassian manages these different levels of requirement with its supplier